Share
0
/5
(
0
)
By 2026, it is anticipated that non-cash transactions in North America only will total 281 billion. Businesses must handle a substantial volume of payments when combined with the anticipated 467 billion transactions in Europe and 1,232 billion in Asia-Pacific. So, almost 2 billion transactions must be taken care of only from these regions.
These corporate operations depend on Payment Service Providers (PSPs). By working with a PSP, businesses can accept client payments using various methods. These companies assist organisations in processing payments quickly and securely by offering a protected web portal, guaranteeing the confidentiality of sensitive payment data during transactions.
In the following sections, we'll look at payment service provider examples, discuss how to choose a PSP for your company and go over the main elements that affect how payment processing systems work. Businesses can choose the right payment service provider for their needs by being informed about the functions and capabilities of these providers.
Key Takeaways
PSPs allow businesses to process lots of payment methods safely.
A trustworthy PSP should be able to manage growing transaction volumes and provide strong security for protecting private financial data.
Selecting a PSP with the appropriate features, such as support for numerous currencies, fraud detection, and easy interaction with current systems, is crucial.
Companies must carefully evaluate PSPs according to price, dependability, and support to ensure the right one is selected for their unique payment processing requirements.
Understanding Payment Service Providers (PSPs)

Customer, business, and bank electronic payment transactions are handled by a Payment Service Provider (PSP). It allows companies to accept payments via various channels, including digital wallets, bank transfers, and credit and debit cards. They operate as middlemen between the financial institutions engaged in the transaction to facilitate the transfer of funds from the customer's account to the merchant's account.
A PSP's primary duty is to establish a secure connection between clients, companies, and banks throughout a transaction. Protecting the transaction details and the customer's financial information involves delivering sensitive payment data over encrypted channels. Sustaining client trust and guaranteeing seamless payment processing depends heavily on this security.
PSPs have changed dramatically with the expansion of e-commerce and electronic payments. Initially, companies used essential payment gateways to process credit card payments. PSPs increased their offerings to include support for many currencies, fraud detection capabilities, and connections with different business systems as the demand for multiple payment methods increased.
The rising complexity of international e-commerce and the requirement for companies to provide their clients with streamlined, safe, and dependable payment options have propelled this development.
PSPs are now essential to the operations of online businesses because they offer more than simply payment processing services; they also provide extra features like currency conversion, recurring payments, and comprehensive transaction reporting.
Due to these developments, PSPs are now essential to contemporary company payment services, allowing businesses to effectively handle and process payments across various channels and geographical locations.
How Does it Work?
As mentioned above, In a transaction, a PSP serves as a go-between for a merchant, a client, and the financial institutions involved. Here's a detailed explanation of how it works:
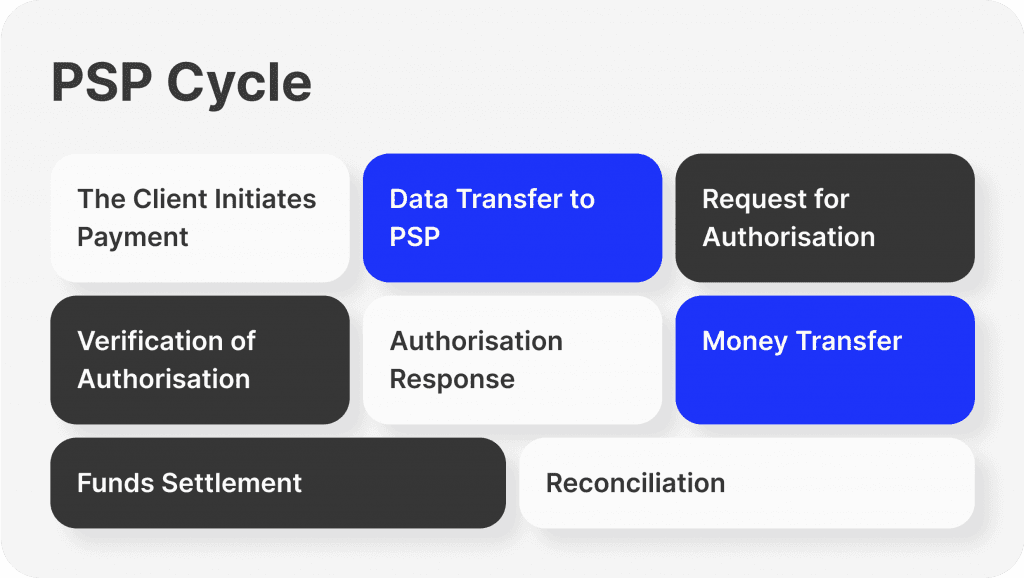
1. The Client Initiates Payment
A consumer buys something from an online retailer. They select the payment solution that best suits them. The payment details are transmitted to the merchant's website via encryption.
2. Data Transfer to PSP
The encrypted payment information is sent to the PSP's payment gateway via the merchant's website.
3. Request for Authorisation
After receiving the payment information, the PSP uses the relevant card network to submit an authorisation request to the bank that issued the cardholder's card, also known as the issuing bank.
4. Verification of Authorisation
The issuing bank confirms the customer's credit limit and available money. If the transaction is accepted, the issuing bank provides the PSP with an authorisation code.
5. Authorisation Response
After receiving the authorisation code, the PSP notifies the merchant via email. Usually, the customer is informed when a transaction is approved.
6. Money Transfer
Following delivery of the products or services, the merchant contacts the PSP to request a settlement. The PSP starts a money transfer from the customer's issuing bank to the merchant's acquiring bank, which controls the merchant's account.
7. Funds Settlement
The acquiring bank credits the transaction value to the merchant's account, less any costs levied by the card networks and PSP.
8. Reconciliation
The PSP gives the retailer comprehensive transaction reports that include details on accepted, rejected, and reimbursed transactions.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a PSP
After understanding the mechanism of PSP, it’s time to break down the characteristics to remember when making a decision.
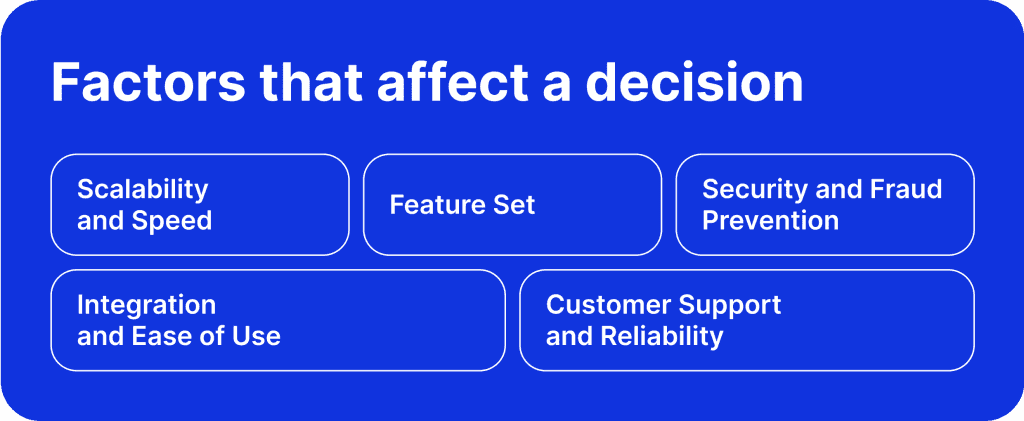
Scalability and Speed
When choosing a PSP, organisations must consider scalability and swiftness. A growing firm's payment processing requirements will also rise, requiring a PSP that can handle higher transaction volumes without sacrificing speed. When operations are busy, a scalable payment processing system keeps things running smoothly and prevents delays that could cause business problems.
A rapid and straightforward connection with your current systems can minimise downtime and disruptions to your business payment services. Thus, assessing the setup procedure and configuration time is critical.
Feature Set
The feature set of a PSP directly affects how useful it is to a company. The best payment service providers accept various payment methods, including alternative ones like Apple Pay and Google Pay, as well as popular credit cards like Visa, MasterCard, and AMEX.
Minimising losses from fraudulent transactions requires effective chargeback management and fraud prevention systems. Businesses may improve overall efficiency and optimise payment operations by leveraging the unique insights that authorisation optimisation and comprehensive reporting capabilities offer into transaction data.
Businesses that wish to perform secure and seamless electronic payment transactions must have these features.
Security and Fraud Prevention
Any business’s success lies in the trust between them and their clients. Robust security protocols are something that build and maintain this trust. Tools and procedures that shield private payment information from cybercrime are essential for a PSP. These technologies should incorporate fraud detection systems, tokenisation, and encryption to reduce the dangers of online payments.
Companies require a payment processing system that guarantees the security of all electronic payments while supporting a variety of currencies and local payment options. Because they guard against fraudulent transactions, fraud prevention systems are essential to maintaining consumer and business trust.
Integration and Ease of Use
A PSP's integration with current corporate systems should be smooth. A key consideration is the ease of use since difficult-to-use or complicated technologies can impede business operations and irritate clients. The appropriate payment service provider should facilitate electronic payment transactions for businesses and their clients.
Businesses can effectively accept payments through a secure online portal or other payment options with an easy-to-use interface and a simple connection process. Several payment options should be supported by this integration, which should also provide seamless channel-to-channel transactions.
Customer Support and Reliability
Any successful PSP must have reliability as its cornerstone, and uptime guarantees (such as 99.99%, 99.99%, and 99.999%) are a crucial sign of service dependability. The best payment service provider must sustain constant accessibility to guarantee uninterrupted payment processing for businesses.
Customer service is also essential, particularly for addressing problems that could occur throughout the payment process. Numerous payment service providers offer round-the-clock assistance, which is crucial for resolving any technical issues that can affect the payment procedure as a whole.
Maintaining efficient operations and high customer satisfaction may be significantly impacted by ensuring dedicated customer care is available.
[aa quote-global]
Fast Fact
Over 900 payment providers operated globally by 2022, with more than 300 serving North America and Europe alone. The worldwide market for online payment service providers is anticipated to increase from $40 billion to $88 billion by 2027.
[/aa]
Selecting a Potential PSP Step-by-Step
Every business decision starts by defining your needs and requirements. Outline the services that your company needs from a PSP. Decide which payment methods, such as credit cards, cryptocurrency, or digital wallets, you must accept. Calculate how many transactions your company anticipates handling. Take care of your main security issues and ensure your sensitive payment data is secure.

Research and Shortlist Potential PSPs
Look carefully to locate PSPs that fit your requirements. Select the three to five providers that most closely match your demands so that you can evaluate them further.
Ask Appropriate Questions to Possible Vendors
Talk to each PSP that was shortlisted to get more precise information. Important questions to ask are:
Which payment options do you accept?
How do you handle fraud prevention and chargebacks?
Which integration possibilities do you have?
Are there case studies or references available from companies like ours?
Assess How to Handle Increases in Transaction Volume
Examine each PSP's ability to handle large transactions, especially during busy periods. Enquire about their response to sudden spikes in transaction volume and the steps taken to ensure steady performance. Ask for examples of the volume increases they have handled for previous clients.
Analyse the cost structure and flexibility
Recognise the pricing structure of every PSP. Consider transaction fees, setup fees, and any ongoing monthly fees. Look into any hidden expenses or extra charges for particular services. Think about how flexible the cost structure is to your company's evolving needs.
Evaluate Capabilities for International Expansion
Make sure the PSP can accommodate any international growth your company may have. Verify the accepted payment methods and currencies. Verify if they provide dynamic currency conversion and multi-currency accounts. Examine their approach to handling foreign rules and compliance.
Verify Availability and Uptime Promises
When processing payments, reliability is crucial. Examine each PSP's claims regarding uptime. Enquire about their promised uptime percentages and their methods for maintaining service continuity in the event of unplanned outages or maintenance. Request incident reports and historical uptime data.
Examine case studies or examples of effective integrations
Request comprehensive case studies for examples of successful PSP integrations with similar firms. For instances of companies identical to yours that have integrated their services successfully, enquire about the difficulties encountered and the payment solutions employed. Recognise the advantages that follow integration.
Carry out a Pilot or Trial Integration
If feasible, conduct a trial or pilot integration to evaluate the PSP's functionality in an actual setting. Find out whether you can perform a trial integration and what kind of assistance you may expect. Specify how you plan to assess the trial's success.
Make an Informed Decision
After gathering all the data, evaluate the PSPs that made the shortlist and select the most suitable option for your company's requirements. Think about how each PSP fits into your needs and long-term objectives. Consider the pros and cons of each choice. Choose the PSP that provides the most features, dependability, and support to accept electronic payments and boost the expansion of your company.
What is the Difference between PSPs and Payment Gateways?
PSPs provide a full range of services that cover all aspects of the payment process, from enabling electronic payments to handling merchant account management and expediting fund retrieval. PSPs are a reliable option for companies seeking an integrated payment processing system since they offer advanced fraud prevention features and automated settlement processes.
On the other hand, payment gateways serve as middlemen that transfer payment data between the customer's bank and the merchant, concentrating on particular payment solutions.

Personalisation Choices
With PSPs, firms may combine their payment operations with other business systems because they offer various customisation choices. This adaptability guarantees that the capacities for processing payments correspond with the particular needs of every company. On the other hand, payment gateways, although providing necessary services, may have restricted customisation capabilities and only serve specific purposes, lacking the more comprehensive flexibility offered by PSPs.
Niche Competencies and Integration Ease
Payment gateways are especially useful for companies that need to handle debit card payments without a lot of extra features or that need to use specific payment methods. They provide simple, easy-to-integrate solutions, particularly for companies with more targeted, minor payment requirements.
Cost-effectiveness
Another critical contrast between PSPs and payment gateways is the cost structure. PSPs that provide an all-in-one solution are typically more costly, with higher monthly expenses and transaction fees because of their various services, such as support for several currencies and a rigorous underwriting procedure.
Payment gateways, on the other hand, are typically less expensive due to their lower monthly and transaction fees. They offer an affordable alternative for companies needing basic payment processing without the complication of advanced fraud prevention or currency conversion services.
Open-Source and White-Label Payment Gateway Considerations
Businesses should weigh their alternatives for open-source or white-label payment gateways when deciding between PSPs and payment gateways. With more flexibility and customisation available with these solutions, companies may adjust the payment system to meet their unique requirements.
Although they need more technical know-how, open-source gateways can offer a more flexible and customisable payment option. With white-label gateways, you can use the technical infrastructure the gateway provider provides and brand the payment system as your own.
Final Thoughts
Any company hoping to process electronic payments effectively must select the appropriate payment service provider.
Businesses need to weigh functionality, pricing, and their unique payment processing capabilities when choosing a PSP. Many providers offer extensive services, but it's critical to select one that meets your particular needs to avoid paying extra for capabilities that aren't necessary or having features that are too complicated.
In the end, your choice should be founded on a detailed comprehension of your company's requirements, backed by precise information and frank evaluations. So, spend some time weighing your options.
FAQ
What is the business model of a PSP?
Through partnerships with acquiring banks and their payment processors, PSPs facilitate the acceptance of payments. They allow it by sending information to the payment processor via a payment gateway.
How should my online store pick the best payment gateway?
Examine the costs associated with using each gateway. Verify the accepted payment methods. Make sure it works with the e-commerce platform you use. Select gateways that provide robust security and efficient anti-fraud measures.
What is a PSP example?
Examples include PayPal, Shopify Payments, Square, Stripe, and Amazon Pay.
Read also







